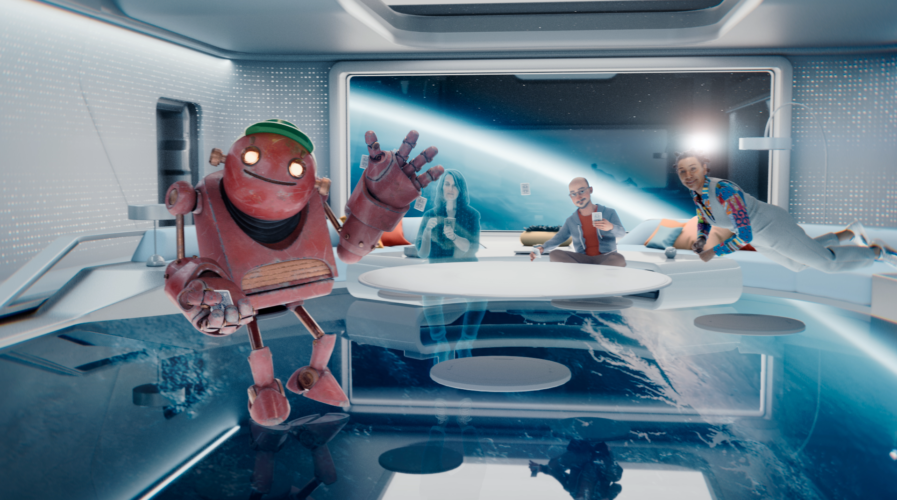
(Source – Meta)
Perfecting the 3D world of the metaverse
For gamers, the 3D world in their games connects them to their gaming universe. And over the years, game developers continue to work on more realistic 3D worlds for gamers, using new technologies like AI imaging, motion capture and such.
Now, the metaverse has been making headlines all over the world. While there have been mixed reactions to it, the reality is, Meta is fully charged to get the metaverse going and create a whole new lifestyle experience for everyone.
Investment firm Morgan Stanley sees the metaverse as an US$8 trillion addressable market which is likely to become the “next generation social media, streaming and gaming platform”. Reports also show that gadgets and wearables in the metaverse being $100 billion in 2030 and growing another five-fold by 2040.
In Asia, the metaverse hype is also going strong with several companies already showing interest in applying similar applications. However, despite the high interest, designing the metaverse is no easy task. In fact, for the metaverse to work properly and give users the full experience, the technology has to be able to provide a realistic experience for users.
Meta has already been developing several wearables for users to experience the realism of the metaverse. But apart from wearables, the atmosphere in the metaverse itself has to reflect the real world. The 3D world of the metaverse is key to ensuring users feel comfortable about using it.
Designing a 3D world involves a lot of image capturing and graphic designing. In most games, the 3D designs make gamers feel they are in the game. The same notion needs to be at the core of the metaverse as well.
Tech Wire Asia speaks to Jon Li, Founder and CEO of Vizzio, a Singaporean start-up that is on a mission to perfect the 3D world in the metaverse.
How will the metaverse impact organizations in Asia?

Jon Li , Founder & CEO, Vizzio.
The metaverse has no doubt been the recent talk of the town. As tech giants such as Facebook and now Microsoft turn the idea of the metaverse into reality, these virtual platforms may soon become our new normal.
Asia is one of the largest digital powerhouses in the world. Home to 2.3 billion internet users, this equates to approximately 50.3% of the global internet user population. As the region’s digital economy continues to grow exponentially, companies in Asia will need to shift gears to deliver digital experiences that are more interactive, immersive and accessible to every individual. That’s where the metaverse comes into play.
Beyond gaming, the metaverse has already touched upon many different vertical industries – for instance, retail, social networking and even urban planning. In Singapore, for instance, the government is building a 3D copy, or rather a digital twin, of the city for designers, planners and policymakers to explore future scenarios.
As Asia progresses on its smart city agenda, it is a key region to watch for developments in the metaverse with increased investment and exploration of the concept. Hence the key question here is not whether the Metaverse will be appealing to organisations in Asia, but rather how we can make this a reality that fulfils its potential.
The concept may be appealing for newer businesses, but will older organizations be able to adapt this?
The great migration to the digital world has accelerated digital transformation for many organizations – be it start-ups, SMEs or large MNCs. What’s great about this is that many organizations are one step closer to the metaverse.
The metaverse concept itself is not new. It has existed in online games such as Second Life. However, that appealed to only a small group of people, i.e. the gamers. With the advent of technology, the metaverse today looks like it will be more inclusive and utilitarian than before in allowing organizations and brands to have better interactions in a virtual world.
In the past, a major hurdle to creating 3D content was the time and resources needed. We have effectively removed these hurdles by helping brands create high-definition content and virtual representations of their organizations or products. This way, adapting to the metaverse need not be a daunting and expensive exercise for any company.
VIZZIO believes that where once was 2D, there will be 3D. Bringing the metaverse to life is not-too-distant in the future and soon enough, every physical element in the world will have a digitized aspect to it – be it an avatar of yourself, a building, or a city. While conversations of the metaverse are now driven by big tech and gaming companies, we will soon see the democratization of this technology where organizations – no matter new disruptors or industry incumbents – will be part of this new digital realm.
How does 3D capture and virtualization technologies play a role in fuelling this virtual world?
The metaverse is very much dependent on 3D capture and virtualization technologies. It’s essentially a Digital Twin of our world and any objects, space and people we see in our everyday lives. Say a bag that you might be carrying to work every day or a landmark attraction in your country. We would need 3D capture and virtualization technologies to create a digital replica of the bag or building, and upload it to this virtual realm.
Our goal is to build the world’s largest 3D capture and virtualization ecosystem by creating the world’s largest database of 3D objects and search capabilities. On that front, we have built a proprietary AI platform that automates the entire process of 3D content creation. Any users – from novices to digital experts across all industries – will be able to access best-in-class 3D-as-a-Service offerings on-demand, and co-create, virtualize and interact with digital realities.
What are the challenges and opportunities in 3D capture and virtualization?

(Source – Meta)
A large part of our digital interactions today still very much depends on 2D imagery. But this is changing with an increasing appetite from consumers, businesses and the public sector. Some examples today include virtual tours of places or a stroll in the metaverse.
While 3D capture and virtualization have been around for a while, the technology remains complex, clunky, expensive and fragmented. To date, even the simplest of 3D models could take hours of meticulous manual input and computer modelling to rendering but may still end up as low definition. This is where VIZZIO hopes to play a part in delivering 3D-as-a-Service offerings on-demand, bridging these gaps and enabling anyone to co-create, virtualize and interact with digital realities.
3D capture and virtualization can be useful in many ways. One of which includes developing predictive models that can analyze environmental changes such as coastal modelling. While there is a deluge of data available for scientists in sustainability planning, visualizing it is a challenge. With the use of 3D virtualization technology, scientists can take the data – from theoretical to practical, and measure predictions or impacts more accurately and efficiently.
How is Vizzio democratizing and simplifying 3D by building the world’s largest 3D capture and virtualization ecosystem, spanning objects, space and cities?
We have been building a suite of hardware and software solutions, backed by our proprietary AI platform, to cover 3D capture for everything from objects to indoor spaces and cities. These include 3D web services/content creation, spatial reality, digital twins, and avatars.
Ultimately, our goal is to significantly reduce the complexities involved in the 3D capture and virtualization process. This will help us save on time and costs while delivering a more accurate and high-resolution product.
Our 3D technologies can be applied to help solve a myriad of global challenges such as:
- Smart city and urban planning: Supporting effective city and urban planning to test efficiencies and optimizations, improve management of resources and build cities of tomorrow.
- Sustainability: Developing predictive models that can analyze environmental changes such as coastal modelling.
- Safety & Security: Enabling better building management planning, safety and/or adherence to regulations. This can include ‘disaster response’ where we support organizations in planning safety routes etc.
- Preservation: Capturing physical cultural heritage sites and objects (e.g. artefacts, statues and art) to preserve for future generations, as well as support research efforts. These captures also enable us to create blueprints and backup replicas.
- Navigation: Location services and navigation with precise indoor and outdoor GPS. This can even go as far as office or event spaces, helping attendees to plan routes – so no more getting lost at trade shows, or on day one of the university.
- Retail: Taking the online shopping and advertising experience to the realms of 3D, enabling consumers to better visualize and interact with products.
Would 4D be the future of the metaverse?
Even in a ‘photorealistic’ virtual world, many things would still remain 3D if we were to savour them in real-time. But what if the future of the metaverse becomes 4D where the time element is incorporated within our virtual experience? The Metaverse could turn 4D when we save our virtual experiences, enabling us to travel into any past experiences. An example of this could be capturing a digital replica of an ancient city or cultural heritage sites where we can “travel back in time” to explore the city and space.
There are a lot of possibilities to explore as we continue to dive into the world of the metaverse. As long as we get the foundation right with 3D capture and virtualization, we will be able to push towards the next frontier of 4D in the metaverse – making the unthinkable a reality.
Lastly, will network latency issues be a problem in the metaverse?
The concept of metaverse means everything is done virtually. In comparison to something that’s similarly dependent on experiences such as video calls and games, users tend to have a lower tolerance for slight network hiccups as it affects their interaction with others. It is due to this social nature of the metaverse that users would be extra sensitive to synchronization issues – judged by something as simple as the seamlessness of facial movement. This means it is essential to ensure that a network works perfectly at all times.
As we build up the metaverse, creating a global ecosystem and partnerships between the key industry verticals will be critical. This way, we can build a network powerful enough to manage the bandwidth needed to support and deliver a seamless metaverse experience to consumers and brands.
With the said, the 3D world of the metaverse seems likely to perfect and enhance the experience for users in the future.
READ MORE
- Ethical AI: The renewed importance of safeguarding data and customer privacy in Generative AI applications
- How Japan balances AI-driven opportunities with cybersecurity needs
- Deploying SASE: Benchmarking your approach
- Insurance everywhere all at once: the digital transformation of the APAC insurance industry
- Google parent Alphabet eyes HubSpot: A potential acquisition shaping the future of CRM