
Gartner predicts that more than 95% of new digital projects will use cloud-native platforms by 2025. (Source – Shutterstock)
Cloud-Native: Can it help businesses or is it overhyped?
- William Dong, Head of Marketing, Huawei Cloud explains how a cloud-native approach can benefit businesses, providing greater efficiency to more customers based on Huawei’s experience as a founding member of the Cloud-Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) in Asia.
As drivers of socioeconomic development, 5G, cloud computing, and AI are seeing broader, more rapid deployment. They are converging fast, driving the digital transformation of industries like energy, transportation, and manufacturing. 2022 saw the rapid adoption of 5G in vertical industries, with more than 20,000 innovative 5G applications put into use. Decarbonization, digitalization, and intelligent transformation are key pathways to sustainable development and predictions highlight the relevance of cloud computing. Also, coordination and collaboration across industries will drive innovation at scale. Predictions by 2030 are as follows:
■ Over 90% of infrastructure will run on the cloud, and more than 85% of all software will be offered as a service.
■ Information and communications technology (ICT) will play a greater role in helping industries boost their energy efficiency, with the potential to cut global carbon emissions by 20%.
■ Intelligent robots will serve more than 18% of homes.
■ Renewables will account for more than 50% of global power capacity.
■ Electric vehicles will become predominant in the automotive industry, accounting for over 50% of new vehicles sold.
What is cloud-native and who is adopting this approach?
Cloud-native represents the most advanced technology direction of cloud computing and a new journey for cloud computing. According to the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF), cloud-native technologies help organizations build and run scalable applications in new dynamic environments such as public, private, and hybrid clouds. Its representative technologies include containers, microservices, service grids, immutable infrastructure, and declarative APIs. Not only Internet enterprises but also large non-Internet enterprises, such as government and enterprises are also migrating to the cloud. Gartner predicts that more than 95% of new digital projects will use cloud-native platforms by 2025, positioning these platforms as a must to dive deep into digitalization.
Why is cloud-native crucial to digital transformation?

William Dong, Head of Marketing, Huawei Cloud
Digital transformation is challenging for the majority of enterprises. It requires a combination of technologies, including all-element data connection, security protection, intelligent decision-making and operations, and knowledge and experience about digital transformation. Cloud is becoming a crucial part of industrial digital transformation with the ability to reshape the economic structure and market landscape of individual industries. The cloud has become application-centric as enterprises have started rethinking how to apply digital technologies to change business applications and transform the customer experience, operating efficiency, and business models.
While many enterprises are currently migrating their applications to the cloud, some remain reluctant or unsure about how to migrate to the cloud, leaving them unable to fully utilize its benefits. This is because cloud services have traditionally been resource-centric, focusing more on infrastructures like compute, storage, and networks.
Huawei Cloud proposed cloud native 2.0 in 2020, which enables applications to be born in the cloud and grow in the cloud. Based on software and hardware collaboration capabilities, full-stack innovative products are opened as cloud services and cloud natives are ubiquitous through distributed clouds. Cloud–native 2.0 not only provides powerful infrastructure for governments and enterprises, but also integrates application development, big data, AI, and media services, and opens 100,000+ industry APIs to accelerate innovation.
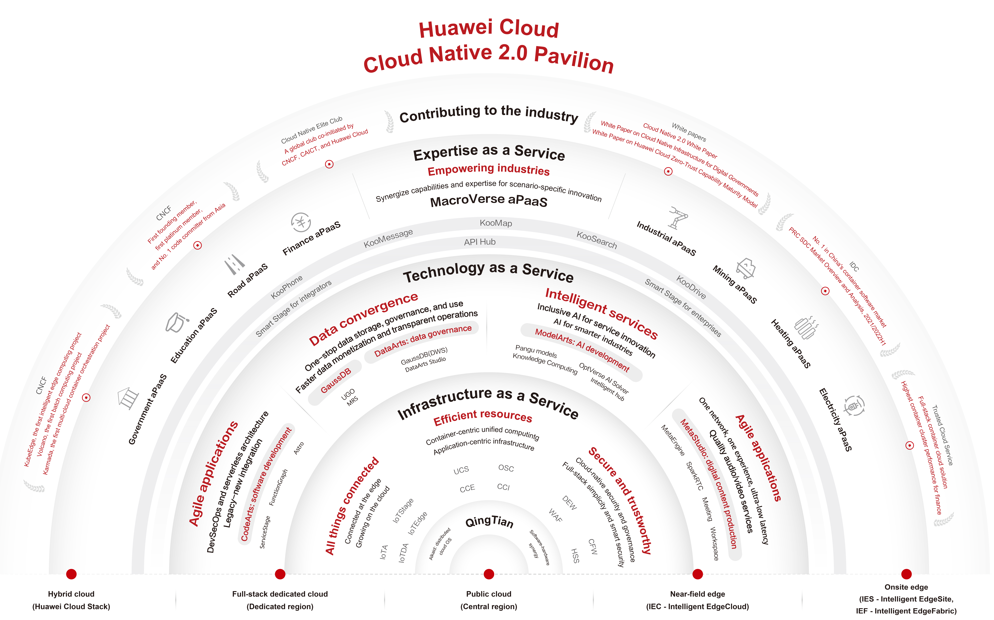
A chart explaining the Huawei Cloud-Native 2.0
Now the cloud is becoming application-centric, and promoting the innovation and evolution of overall cloud technical architecture. Here are some examples:
Finance
The finance industry has extremely strict data security requirements. Eliminating concerns about public cloud security prompted banks to start building reliable platforms with systematic security protection provided by cloud vendors, covering technologies, personnel, operations, and processes. These platforms possess fully-integrated, cloud-native capabilities such as resource elasticity, agile innovation, and high concurrency. In Thailand, one century-old bank was able to develop a new service for digital growth gaining 45,000 online customers within three months of launch and approval of loans in just five minutes.
Automotive
The automotive industry is undergoing enormous transformation including coping with due the proliferation of data created by connectivity and intelligence. By leveraging elastic cloud-native infrastructure resources, one automaker has been able to allocate more computing power during peak travel hours of connected vehicle services and reduce computing power at night. Flexible resource allocation and dynamic resource adjustment based on business requirements reduce cloud service costs by more than 40%. More importantly, the automaker has expanded its business scope using technologies based on big data and artificial intelligence resulting in many innovative services such as UBI auto insurance, auto finance, smart after-sales, and intelligent manufacturing.
Manufacturing
The demand for development of the manufacturing industry has driven enterprises to strengthen R&D innovation and smart manufacturing. Reconstruction software and hardware development tools (such as CAD, CAE, and EDA) using cloud native technologies allow traditional team collaboration approaches to change from an offline process of “independent design-project combination-optimization iteration” to online sharing, collaboration, and real-time optimization. This has greatly increased the speed of R&D innovation. For example, the industrial IoT platform, big data, and artificial intelligence on the cloud are used to build digital twins of factories. AI can be widely used in the manufacturing industry through the implementation of industry models, intelligent production scheduling, quality inspection, and logistics to improve production efficiency and product yield. This improvement in productivity is driving digitalization.
Migration to Cloud Native – Considerations
- Energy conservation & reducing carbon emissions: Your data center site should be low-carbon with a green power supply and intelligent site operations to minimize power use.
- Improved resource utilization: Cloud-native will facilitate one-stop coordination of organization and accounts, finance, compliance and audit and professional services.
- Financial management: Enterprises are still facing huge challenges in financial management. The basis of cloud financial management is to establish a cost accountability system, which ensures that departments, business teams, and owners are accountable for their respective costs.
- Allocating cloud expenditures to identify cost sources and track cost changes
- Accurately forecasting costs and planning budgeting
- Tracking and controlling expenditures more to keep projects within their budgets
- Identifying things that are over budget and optimizing cloud costs
Migrating to cloud-native has become relevant across all sectors allowing traditional industries greater innovation through network convergence and flexibility.
READ MORE
- Safer Automation: How Sophic and Firmus Succeeded in Malaysia with MDEC’s Support
- Privilege granted, not gained: Intelligent authorization for enhanced infrastructure productivity
- Low-Code produces the Proof-of-Possibilities
- New Wearables Enable Staff to Work Faster and Safer
- Experts weigh in on Oracle’s departure from adland


