
Google Bard just released a huge update. (Image – Shutterstock)
Google launches Bard Extensions for its apps and services
- Google is now letting users double-check their responses generated on Google Bard.
- Google’s Bard Extensions allows users to use Bard alongside Google apps and services easily.
- Google is hoping to challenge ChatGPT with Extensions.
It’s been almost six months since Google Bard made its debut. Despite some initial glitches the app had when showcasing its capabilities, Google Bard has grown in popularity over the first half-year of its existence. In fact, since its launch in March 2023, Google Bard has had an average of 140.6 million monthly visitors.
Leveraging LaMDA, the conversational generative AI chatbot currently supports more than 40 languages and is available almost everywhere. Google’s main rivals are Microsoft’s Bing and OpenAI’s ChatGPT. While several other tech companies are also developing and releasing similar AI chatbots, the industry is dominated mainly by that trio: Microsoft, OpenAI, and Google.
While ChatGPT is focused more on creating content based on prompts, Bard and Bing were also implemented into search engines to help users get better search results. However, all three generative AI chatbots had one problem – their answers were not as good as they were meant to be. Users of these platforms soon had inaccurate results for some of their prompts and queries.
This phenomenon is known as AI hallucination. AI hallucinations occur when large language models make up false information or facts that aren’t based on real data or events. Avivah Litan, a VP analyst at Gartner, explained that hallucinations and fabrications, including factual errors, are some of the most pervasive problems emerging with generative AI chatbot solutions.
“Training data can lead to biased, off-base, or wrong responses, but these can be difficult to spot, particularly as solutions are increasingly believable and relied upon,” said Litan.
Google CEO tweets about Bard Extensions.
Fixing hallucinations and misinformation
To deal with this, Google lets users double-check the responses generated on Google Bard. Yury Pinsky, director of product management for Bard, explains that answers in English can be double-checked with Bard’s Google It button.
“When you click on the “G” icon, Bard will read the response and evaluate whether there is content across the web to substantiate it. When a statement can be evaluated, you can click the highlighted phrases and learn more about supporting or contradicting information found by Search,” explained Pinsky.
For example, a user uses Bard to plan their travel schedule. Bard’s suggestions may include places that may be crowded or closed during certain hours of the day. The user can click on the G icon to get a more accurate schedule and better plan for their journey.
While some may argue that this feature does not do much, or indeed that it should be possible to simply refine out the hallucinations on the first pass, Bard’s double-checking function could make a difference for many use cases. Employees using Bard at work or students using Bard for research could find this update beneficial.
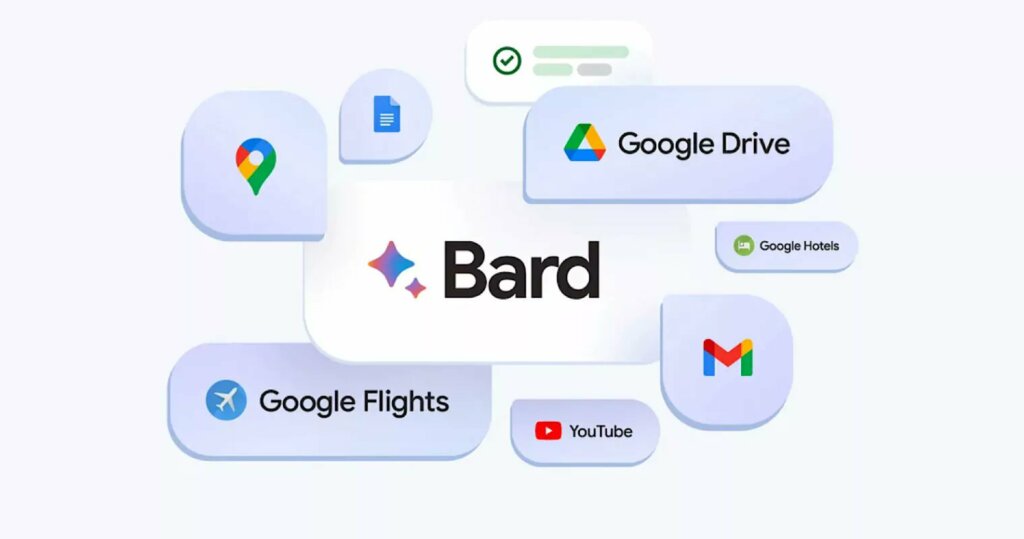
Use Bard alongside Google apps and services. (Image – Google)
Bard Extensions
Apart from the double-checking features, Google also announced Bard Extensions. With Bard Extensions, users can now easily use Bard alongside Google apps and services. Bard Extensions will connect to a user’s Gmail, Docs, Drive, Google Maps, YouTube, and even Google Flights and Hotel.
Bard Extensions’ capabilities are similar to what Microsoft does with its Office 365 apps. However, Microsoft’s capabilities come with a cost and are not currently available through the Bing chatbot.
As always, there will be privacy concerns with Bard Extensions. Given the tools’ abilities to access emails and almost every other private information or personal content on Google Apps, some users might be concerned about how Google has access to and handles all this information.
To this, Pinsky responded: “We’re committed to protecting your personal information. If you choose to use the Workspace extensions, your content from Gmail, Docs, and Drive is not seen by human reviewers, used by Bard to show you ads, or used to train the Bard model. And, of course, you’re always in control of your privacy settings when deciding how to use these extensions, and you can turn them off at any time.”
A challenge for ChatGPT?
Can Bard catch ChatGPT?
Google’s Bard Extensions is an example of how Google hopes to catch up with ChatGPT in the generative AI field. Despite recording increasing traffic, Bard is still nowhere near ChatGPT in terms of popularity. ChatGPT traffic remains high, despite some reports stating that it has recently fallen.
According to a report by Reuters, worldwide desktop and mobile website visits to the ChatGPT website decreased by 3.2% to 1.43 billion in August, following approximately 10% drops on each of the previous two months. The amount of time visitors spent on the website has also been declining monthly since March, from an average of 8.7 minutes on site to 7 minutes on site in August.
But these figures are still a lot higher than what Bard is experiencing. While it may be some time before Google catches up, it is doing all it can to remain a relevant competitor.
At the end of the day, users will want a platform that can guarantee them an excellent conversational AI experience and ensure their privacy. That’s something both companies are still trying hard to achieve.
READ MORE
- Safer Automation: How Sophic and Firmus Succeeded in Malaysia with MDEC’s Support
- Privilege granted, not gained: Intelligent authorization for enhanced infrastructure productivity
- Low-Code produces the Proof-of-Possibilities
- New Wearables Enable Staff to Work Faster and Safer
- Experts weigh in on Oracle’s departure from adland






