
How can we counter the rising wave of cyber threats?
How vulnerable are we to cyber threats in the digital age? Here’s what IBM found
- 2023 saw a surge in cyber threats, with Malaysia among the top breached countries and a daily average of 74,000 attacks globally.
- AI emerges as a crucial tool in combating and accelerating cyber threats.
- A comprehensive security approach is vital for safeguarding against increasing attacks.
In the first half of 2023, a report from CyberSecurity Malaysia reveals a concerning trend: the government sector has experienced the highest number of data breaches, while the telecommunications sector has seen the largest volume of data leaked. This data underscores the pressing challenges in protecting sensitive information across different sectors.
National and global cybersecurity challenges
By October 2023, the National Cyber Coordination and Command Centre (NC4), under the auspices of the National Cyber Security Agency, had already registered close to 3,000 cyber incidents, highlighting the increasing focus on cybersecurity matters within the nation. Adding to the concern, cybersecurity firm Surfshark placed Malaysia as the eighth most breached country in the third quarter of 2023, with nearly half a million accounts compromised.
The frequency of cyber threats became even more pronounced, with statistics showing that there have been 74,000 attacks daily throughout the year. In a particularly alarming revelation by both Kaspersky and Surfshark, the rate at which Malaysian user accounts were compromised in Q3 2023 amounted to four leaks every minute.
This data not only underscores the urgency of the cybersecurity situation but also emphasizes the importance of understanding attackers’ tactics to safeguard our people, data, and infrastructure effectively.
Shifting the focus to a global perspective, IBM’s 2024 X-Force Threat Intelligence Index unveils a similar urgency in addressing cybersecurity threats. IBM has unveiled a growing global identity crisis caused by cybercriminals increasingly exploiting user identities to infiltrate enterprises worldwide. This report draws on observations from monitoring over 150 billion security events daily across more than 130 countries.
The emerging crisis is stark: cybercriminals are shifting from hacking online accounts to using readily available internet and dark web data, with AI further simplifying these breaches. This shift allows for deeper incursions into personal lives, exposing everything from daily routines to hobbies and interests.
IBM X-Force, the offensive and defensive security services branch of IBM Consulting, noted a significant shift in 2023. Cybercriminals preferred using legitimate account credentials to breach corporate networks rather than hacking, making this strategy a favorite among threat actors.
Asia-Pacific cybersecurity landscape
The 2024 X-Force Study also provides a geographical breakdown of cyber incidents, with the Asia-Pacific region being the third most impacted in 2023, accounting for 23% of global incidents handled by X-Force. This marked a change from 2021 to 2022, when Asia-Pacific was most affected. In 2023, Europe rose to the top spot, with 32% of incidents, followed by North America at 26%, Asia-Pacific at 23%, Latin America at 12%, and the Middle East and Africa at 7%.
In the Asia-Pacific, manufacturing continued to be the industry most targeted by cyber attacks for the second consecutive year, comprising 46% of incidents. Finance, insurance, and transportation industries followed, each representing 12% of incidents, and education came in third at 8%.
Phishing remained the predominant method for gaining initial access, responsible for 36% of incidents, closely followed by attacks on public-facing applications at 35%.
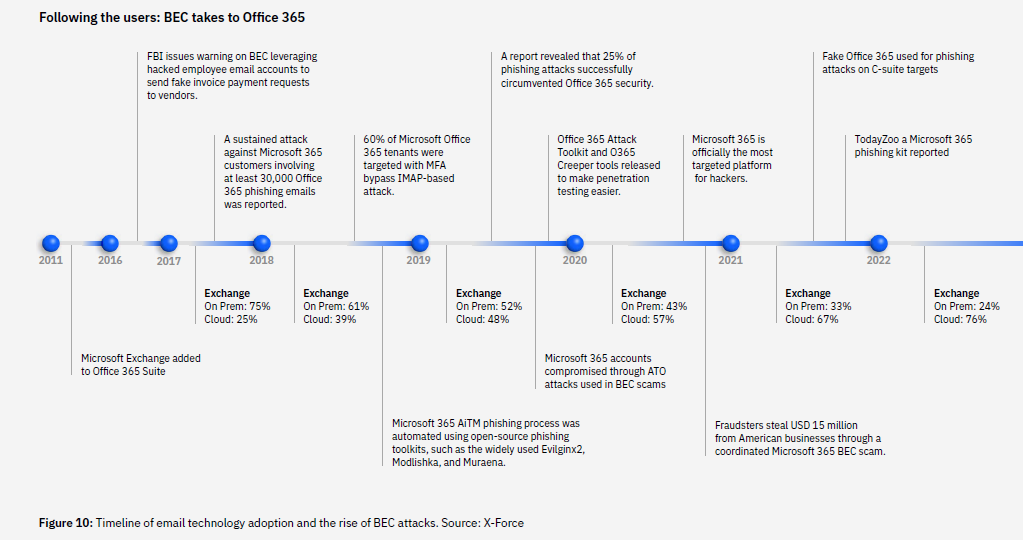
Phishing in action (Source – IBM)
Once inside, malware was the leading action, with 45% of attacks involving this tactic, including ransomware (17%) and info stealers (10%).
The report suggests that the return on investment (ROI) from attacking generative AI platforms isn’t significant yet. However, X-Force anticipates large-scale attacks on these technologies once a single AI gains 50% market share or the market narrows down to three or fewer competitors.
Despite a 44% drop in phishing attack volume from the previous year, phishing remains a primary method of attack, particularly as AI can refine and accelerate these attacks by nearly two days, keeping it a preferred method among cybercriminals.
The role of AI in dealing with cyber threats
Amidst these cybersecurity challenges, AI emerges as a pivotal tool in both exacerbating and combating threats. AI is now widely recognized for its utility, especially in how it has revolutionized threat detection, response times, and the protection of user identities and data flow. According to the IBM Cost of Data Breach 2023 report, organizations worldwide have saved almost US$1.8 million on data breach costs by leveraging AI and automation, compared to those that haven’t embraced these technologies.
However, the advent of generative AI introduces new challenges and opportunities in both attacking and defending enterprise assets. As the AI capabilities of attackers evolve, we can expect their attacks to become faster, more precise, and scalable. Conversely, AI is also poised to boost the productivity of enterprise security, with its ability to quickly identify and prioritize threats like ransomware based on their signatures and behaviors—even if it’s a variant the system hasn’t encountered before.
Generative AI, with its capacity for self-learning, doesn’t require prior exposure to specific scenarios to detect new, sophisticated threats. This aspect makes it invaluable for cybersecurity, where it accelerates business processes by automating threat detection and investigation and adapts real-time organizational response strategies based on past incidents. It frees up security teams to tackle more complex and strategic security challenges.
The 2024 X-Force study suggests that as generative AI gains market dominance, it could also become a focal point for cybercriminals, encouraging further investment in tools designed for AI-engineered attacks. Despite the growing concern over such attacks, the primary security threat in the Asia Pacific region remains the exploitation of known, unpatched vulnerabilities.
Attention must also be directed towards protecting the region’s critical infrastructure and key sectors like manufacturing, finance, insurance, and transportation. This includes conducting stress tests and having a robust incident response plan ready.
With the increasing preference among global threat actors for exploiting user identities, there’s a pressing need for more effective user access control measures. This scenario underscores the importance of a comprehensive approach to security in the era of generative AI, highlighting the need for heightened vigilance and adaptation in cybersecurity strategies.
Strategic cybersecurity measures to prevent malicious cyber threats
Various strategies can mitigate cybersecurity threats, and it’s crucial to choose the one that best aligns with your specific needs or those of your business. While numerous AI solutions claim to offer protection against a wide array of cyber threats, the choice ultimately depends on what aligns best with your or your business’s specific needs. For instance, the IBM X-Force Threat Intelligence Index 2024 highlights insights and actionable recommendations for enhancing readiness and improving the speed and efficiency of response to cyberattacks.
One effective approach is to update identity management across multicloud environments. As cybercriminals increasingly exploit legitimate user accounts to gain access to networks—accounting for 30% of incidents responded to by X-Force in 2023—strengthening identity and access management (IAM) becomes crucial. Solutions like IBM Security Verify can bolster security in hybrid and multicloud setups by providing comprehensive IAM capabilities.
Beyond identity management, AI plays a critical role in optimizing cybersecurity resources. Tools such as IBM Security QRadar SIEM User Behavior Analytics (UBA) can aid in identifying compromised credentials and malicious activities, allowing teams to utilize their skills and time better. IBM Security QRadar EDR further enhances protection by securing endpoints and detecting unusual activities, such as data exfiltration or unauthorized account creation.
This pivot from ransomware to malware, particularly those targeting data theft, underscores the imperative of safeguarding data across hybrid cloud environments. This shift underscores the need for vigilant monitoring and robust data protection measures.
However, increasing security spending alone may not suffice. Embracing a zero-trust model and prioritizing trusted data can bolster your cybersecurity posture significantly. By fostering transparency and accountability, organizations can not only minimize risks but also actively prevent bias, making the zero-trust model and prioritization of trusted data essential strategies.
In light of these strategies, building trust and preparing for future threats become pivotal. A proactive security stance, grounded in careful partner selection and regular security reviews, complements the technical and strategic measures discussed. Building trust should be the foundation of every interaction, enhancing cyber-risk management and prioritizing cyber resilience to maintain and strengthen business relationships. This involves constantly monitoring and managing crucial points where trust is established or compromised.
Preparing for future threats requires a proactive security stance, including careful selection of partners and regular reviews of their security strategies and practices. This comprehensive approach to cybersecurity emphasizes the need for a balanced mix of technology, strategy, and a culture of trust and resilience.
As we prepare for future threats, a balanced mix of technology, strategy, and a culture of trust and resilience is crucial. The comprehensive approach discussed underscores the need for vigilance and adaptability in cybersecurity strategies to combat the evolving threat landscape effectively.
READ MORE
- Safer Automation: How Sophic and Firmus Succeeded in Malaysia with MDEC’s Support
- Privilege granted, not gained: Intelligent authorization for enhanced infrastructure productivity
- Low-Code produces the Proof-of-Possibilities
- New Wearables Enable Staff to Work Faster and Safer
- Experts weigh in on Oracle’s departure from adland


