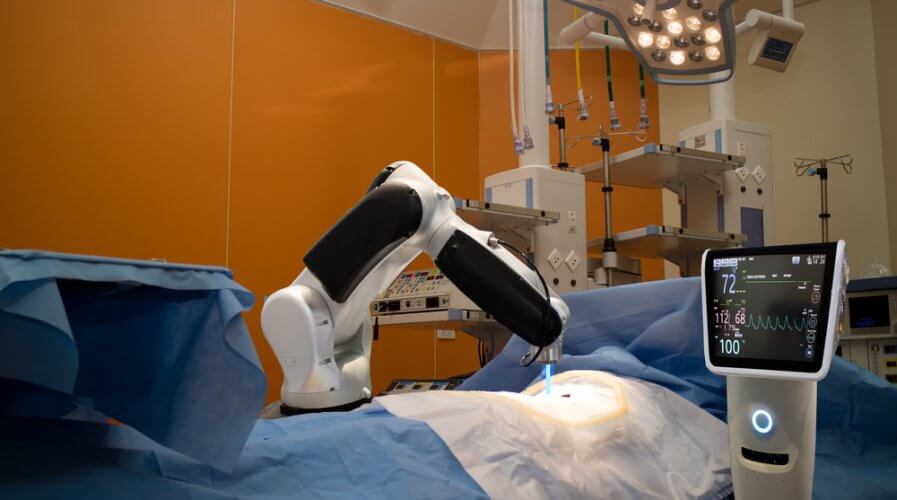
5G can make it possible for doctors to remotely perform surgery via robots. Source: Shutterstock
Why healthcare professionals are keen on leveraging 5G in 2020
IN COUNTRIES where the doctor to public ratio is low — like in China and Indonesia — 5G can play a prominent role in helping healthcare professionals boost access to better medical facilities.
By itself, 5G might not be able to move the needle by much, but it enables technologies such as the internet of things (IoT), high-definition video for augmented and virtual reality (AR and VR), and high-precision robotic arms that can collectively transform the possibilities for healthcare companies.
According to recent studies, as the industry begins a shift in focus from volume-based healthcare to value-based (outcome-based) healthcare, the world could save up to US$650 billion by 2025 — and naturally, 5G is expected to be a major facilitator of that change.
Further, according to IHS Markit, 5G will enable more than US$1 trillion dollars in products and services for the global healthcare sector.
Here are three of the most important use cases for 5G as expected by healthcare professionals:
# 1 | Transforming wearables
The current generation of wearable devices can monitor patients quite well, but connectivity and battery life are still an issue.
In fact, according to a recent study, 59 percent of consumers say that they are concerned about poor connectivity affecting data transmission and 56 percent of consumers with chronic ailments worry about their health patches suddenly running out of battery.
However, 42 percent of the cross-industry decision-makers surveyed expect that devices connected to 5G networks will consume less power, reducing the frequency of recharges.
In the future, once 5G networks are live, patients will be able to rely on wearable devices to continually capture, collect, and electronically transmit patient medical data to healthcare professionals without network failures or battery issues.
Important metrics such as vital signs, physical activity, and even ingestion of prescribed medication can be monitored electronically. Healthcare professionals can then use this data to remotely make decisions about next steps for patients.
In fact, the Internet of Medical Things is expected to grow as the patient-monitoring wearable market, which includes remote and on-site devices, expands from 8 million shipments (from last year) to 33 million in 2021.
# 2 | Harnessing VR and AR
Thanks to the strong infrastructure provided by 5G, healthcare professionals can remotely check on their patients using AR and VR, and even perform surgery on them.
This application is currently being explored by several institutions and has even been discussed by healthcare professionals in China recently — at the Huawei Asia Pacific Innovation Day in Chengdu, China.
Further, 5G can also support the training of doctors and practitioners. QTI, for example, is producing a medical VR experience to train medical students on the physiology and diagnosis of stroke, using VR to enable medical students to walk a virtual pace through a stroke exam.
# 3 | Leveraging robotics
According to experts, a prominent use of 5G for healthcare will be to enhance patient care and health informatics with greater connectivity through live-in robots that facilitate telemedicine to provide constant critical care to patients.
When the robot is connected, a doctor can give instructions for it to visit the patient’s bedside. Using the robot’s two-way audio-visual teleconferencing feature, the doctor and patient can interact and share medical information easily and naturally.
This use case is in addition to the existing remote, high-precision robotic arm surgeries trials that healthcare institutions are exploring, with help from 5G networks.
READ MORE
- Strategies for Democratizing GenAI
- The criticality of endpoint management in cybersecurity and operations
- Ethical AI: The renewed importance of safeguarding data and customer privacy in Generative AI applications
- How Japan balances AI-driven opportunities with cybersecurity needs
- Deploying SASE: Benchmarking your approach


