
Source – Shutterstock
What good is ChatGPT if less-skilled threat actors could use it to launch cyberattacks?
|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready... |
- According to Check Point Research, cybercriminals are already leveraging OpenAI to create malicious tools.
- ChatGPT is reportedly unavailable in many countries and territories due to security concerns.
Remember when people were going crazy for ChatGPT? The platform was used in many cases, allowing individuals to express their creative minds through an AI-generated conversation platform. Despite their usefulness, threat actors exploit the platform for evil.
How threat actors recognize ChatGPT as an assistant.
As soon as it was realized that code generation might make it simple for less skilled threat actors to initiate cyberattacks, ChatGPT added some spice to the current cyber threat landscape.
One common way that less-skilled threat actors utilize ChatGPT is by creating automated chatbots for phishing campaigns. These chatbots are programmed to engage with victims in real-time conversations, using ChatGPT to generate convincing responses. They may ask victims to enter their login credentials or other sensitive information, which the attacker then collects.
In Check Point Research’s (CPR) first blog post on the topic, the team revealed how ChatGPT successfully carried out a full infection flow, from crafting a plausible spear-phishing email to operating a reverse shell that could accept commands in English. The question is whether this threat is only theoretical or whether threat actors are already utilizing OpenAI technologies for malicious reasons.
According to CPR’s investigation of numerous major underground hacking communities, cybercriminals are already leveraging OpenAI to create malicious tools. As CPR had predicted, some examples made it evident that many of the cybercriminals using OpenAI lacked any programming knowledge.
Case 1 – Creating an infostealer.
On December 29, 2022, a renowned underground hacking forum saw the appearance of a thread titled “ChatGPT – Benefits of Malware”. The thread’s creator revealed that he was using ChatGPT to test out malware strains and strategies that were documented in research publications and articles about common malware. For example, he shared the source code for a Python-based stealer that looks for popular file types, transfers them to a random folder inside the Temp folder, zips them up, and uploads them to a pre-programmed FTP server.
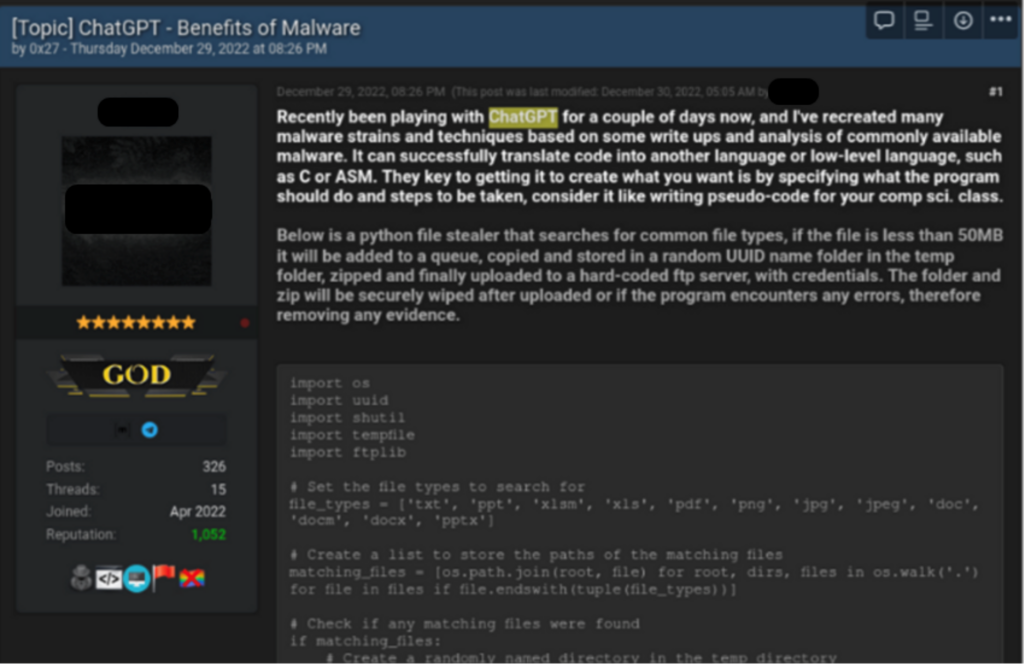
Cybercriminal showing how he created infostealer using ChatGPT.
The script’s analysis by CPR supports the cybercriminal’s assertions. This basic stealer scans the system for 12 common file types, including photos, PDFs, and MS Office documents. If any files are discovered, the malware copies them to a temporary directory, zips them, and sends them over the internet. It is important to note that the actor neglected to encrypt or deliver the information securely; therefore, the files may also end up in possession of third parties.
Overall, this person comes out as a tech-oriented threat actor, and his posts aim to provide practical examples that less technically skilled hackers may use to learn how to use ChatGPT for nefarious purposes.
Case 2 – Creating an encryption tool.
On December 21, 2022, a threat actor going by the handle USDoD submitted a Python script emphasizing that it was the first script he had ever written.
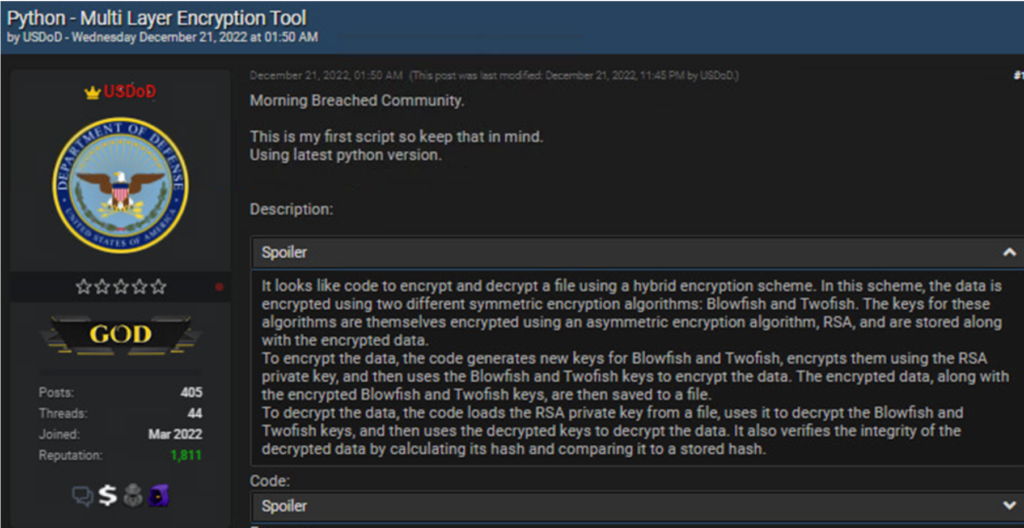
Cybercriminal dubbed USDoD posts multi-layer encryption tool.
When another cybercriminal commented that the style of the code is similar to openAI code, the USDoD acknowledged that the OpenAI offered him a “good [helping] hand to finish the script with a nice scope”.
CPR’s analysis established that it is a Python script that executes cryptographic operations. To be more precise, it combines a variety of signing, encryption, and decryption operations.
It’s worth noting that the script includes all the decryption functions corresponding to the encryption functions. This script can be changed automatically and encrypt a user’s machine. If the script and syntax errors are rectified, for instance, it could be possible to turn the code into ransomware.
Case 3 – Facilitating ChatGPT for fraud activity.
At the start of 2023, several threat actors started threads in more dark web forums discussing how to exploit ChatGPT for fraudulent schemes. Most of these centered on producing random art using another OpenAI technology (DALLE2) and selling it online via reputable marketplaces like Etsy. In a different example, the threat actor describes how to create a small chapter or e-book for a specific topic (using ChatGPT) and then sells this information online.
Multiple threads in the underground forums on how to use ChatGPT for fraud activity.
Certain countries don’t have access to ChatGPT, because of security reasons.
In some cases, nations might not be allowed to access specific websites or technology due to security concerns. The website or technology in question might be the cause because it could endanger national security by facilitating acts that could undermine the country’s stability or grant access to potentially dangerous information.
Due to security concerns, ChatGPT is reportedly unavailable in many countries and territories. The nations without access to ChatGPT and GPT-3 technology are listed below:
- China
- Russia
- Ukraine
- Afghanistan
- Iran
- Belarus
- Venezuela
Multiple users from Egypt also have complained that they cannot access the chatbot. Along with Russia and Iran, the company has listed Ukraine as a terrorist country. It makes sense that governments would take action to restrict access to such websites or technology to safeguard their citizens and uphold public safety.
It’s still too early to say whether ChatGPT capabilities will replace other popular Dark Web tools as the preferred option. However, the cybercriminal community has already expressed a lot of interest and is embracing this latest development to produce malicious code.
READ MORE
- Safer Automation: How Sophic and Firmus Succeeded in Malaysia with MDEC’s Support
- Privilege granted, not gained: Intelligent authorization for enhanced infrastructure productivity
- Low-Code produces the Proof-of-Possibilities
- New Wearables Enable Staff to Work Faster and Safer
- Experts weigh in on Oracle’s departure from adland


