Fake ChatGPT domains are increasing – When will it stop?
- ChatGPT’s popularity has spawned many fake domains, APKs, and browser extensions claiming association.
- Technisanct researchers found 7946 domains registered under ChatGPT’s name, a concerning number.
In recent years, the rise in demand for artificial intelligence (AI) and natural language processing (NLP) has resulted in the creation of several chatbot services. One of the most prominent AI chatbots is ChatGPT, a large language model OpenAI has trained.
Nonetheless, the increasing popularity of ChatGPT has led to the emergence of multiple fake domains, APKs, and browser extensions that claim to be linked with ChatGPT. These fraudulent domains, apps, and browser extensions are designed to deceive users into downloading and installing harmful software, stealing their personal information, or otherwise compromising their devices.
Technisanct’s report highlights different types of fake ChatGPT domains and browser extensions, as well as the methods used by malicious actors to lure users into downloading or installing these malicious tools.
The rise of AI chatbots and emergence of fake domains and browser extensions
As the use of AI and NLP technologies grows, it has given rise to fraudulent domains, applications, and browser extensions designed to deceive users into installing harmful software, stealing personal information, or otherwise compromising their devices.
The emergence of these fake ChatGPT domains and browser extensions is a result of the increasing use of these technologies, providing attackers with new opportunities to exploit users’ trust. Attackers employ social engineering tactics, such as creating convincing logos and web pages and using persuasive language in marketing materials, to deceive users into installing fake ChatGPT apps.
The researchers at Technisanct have revealed an alarming 7946 domains registered with ChatGPT in their name, with 5549 of those domains beginning with “chatgpt.” A significant number of these domains are utilized for hosting malicious software or phishing schemes that can result in severe outcomes for unsuspecting users.
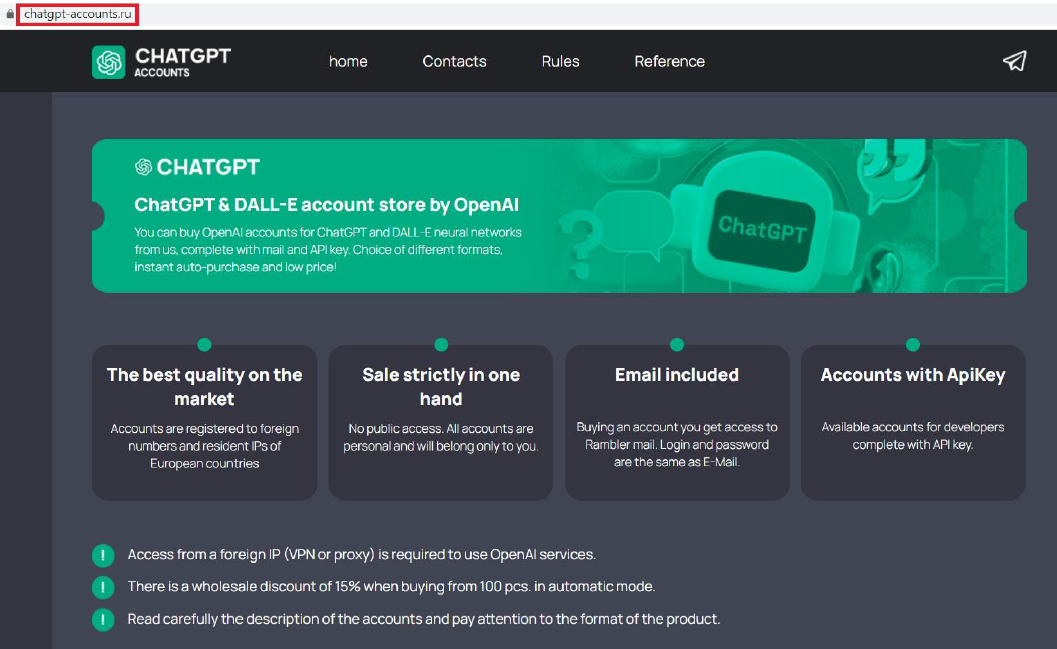
Source – Technisanct
The research team have also identified some ChatGPT Chrome extensions that raise suspicion by requesting risky permissions. These unauthorized third-party extensions could potentially install malware on users’ devices, obtain access to their personal information, or contain malicious code to engage in criminal activities.
Risks associated with fake ChatGPT domains and browser extension
There has been a rise in the use of stealer malware by threat actors to obtain credentials from users’ devices. This type of malware can steal sensitive information such as cookies, credit card details, cryptocurrency wallets, and other personal data stored on the victim’s device. The malware uses various techniques to gather information from the user’s computer.
Fake ChatGPT domains and browser extensions can cause various forms of harm to users. Some of the risks include:
- Malware: these fraudulent domains and extensions can distribute malware, which may be used to obtain sensitive information, spy on users, or take control of their devices.
- Phishing: malicious actors can use fake ChatGPT domains and browser extensions to deceive users into sharing confidential information such as login credentials, personal information, or financial details, leading to identity theft or other types of fraud.
- Financial loss: fraudulent ChatGPT domains and browser extensions can also be employed to carry out fraudulent activities, such as unauthorized purchases with credit cards or stealing money from bank accounts.
- Reputation damage: victims of scams or malicious activity through fake ChatGPT domains and browser extensions risk reputational harm, especially if it involves sensitive information or financial losses.
Methods used to lure users
Below are some commonly used methods by malicious actors to entice users to download or install fake ChatGPT domains or browser extensions:
- Phishing emails or messages: malicious actors may send emails or messages that resemble those from ChatGPT, requesting users to download a particular application or share sensitive information.
- Fake promotions or giveaways: malicious actors can create fake promotions or giveaways related to ChatGPT, demanding users download an application or provide personal information to take part.
- Search engine optimization (SEO) manipulation: malicious actors can employ SEO tactics to make their fake domains or applications rank higher in search engine results for relevant keywords, making them more likely to be clicked.
- Social engineering: malicious actors can use social engineering methods to deceive users into installing fake applications or sharing sensitive information, such as impersonating a trusted friend or authority figure.
Users must be aware of the risks associated with downloading and installing fraudulent ChatGPT apps and browser extensions and take appropriate precautions to avoid falling prey to malicious tools.
READ MORE
- Safer Automation: How Sophic and Firmus Succeeded in Malaysia with MDEC’s Support
- Privilege granted, not gained: Intelligent authorization for enhanced infrastructure productivity
- Low-Code produces the Proof-of-Possibilities
- New Wearables Enable Staff to Work Faster and Safer
- Experts weigh in on Oracle’s departure from adland


