
(Photo by Hector RETAMAL / AFP)
Apple’s market share peaked in China — with 1 in every 4 devices sold being iPhone
- In October 2022, right before the unrest in the iPhone city in China, Apple reached its highest ever monthly market share, dominating 25% of the local market.
- While the sales for other key OEMs declined in October, Apple grew 21% MoM, emerging as a clear winner of Huawei’s share in the premium market.
- The rise has made Apple the number one OEM in the country for the second consecutive month.
Apple successfully became the top original equipment manufacturer (OEM) in China for the second consecutive month in October, the same month the iPhone maker saw its market share peak to its highest ever in the country. A report by Counterpoint research highlighted that one in every four devices sold in China during October 2022 was an iPhone. The feat, one that local analysts reckon as ‘inevitable’, came just before protests against Covid-19 restrictions at Apple contract manufacturer Foxconn’s flagship factory in Zhengzhou broke out.
The Cupertino, California-based tech giant grabbed a 25% share of the smartphone market in China two months ago, thanks to the popularity of its newly released iPhone 14 series. That same month, The iPhone 14 Pro Max was the best-selling device in China, followed by the iPhone 14 Pro. October also marked the first full month of iPhone 14 series sales.
The success by Apple came in time when the sales for other key OEMs declined. For context, in year-on-year (YoY) terms, China’s sales declined 15%, while Apple’s sales declined just 4%, further helping increase Apple’s market share. “China’s market has been sluggish due to multiple factors, including macroeconomic pressures and COVID-19 lockdowns hitting consumer sentiment. Overall sales declined 4% MoM,” Research Director Ethan Qi said in a statement.
Apple grew 21% month-on-month (MoM), but has been reaching new heights in terms of market share in China for the last two years. It reached a record monthly market share in November and December 2020, and in October, November, and December 2021. It is important to note that 2020 was also the year when US sanctions were imposed on Huawei.
“Apple managed to defy the market trend. This also shows the resilient nature of the premium segment. Looking at the trend for the last two years in China, it is evident that Apple has emerged as a clear winner of Huawei’s share in the premium market. It has almost become an undisputed leader in China’s premium segment,” Qi added.
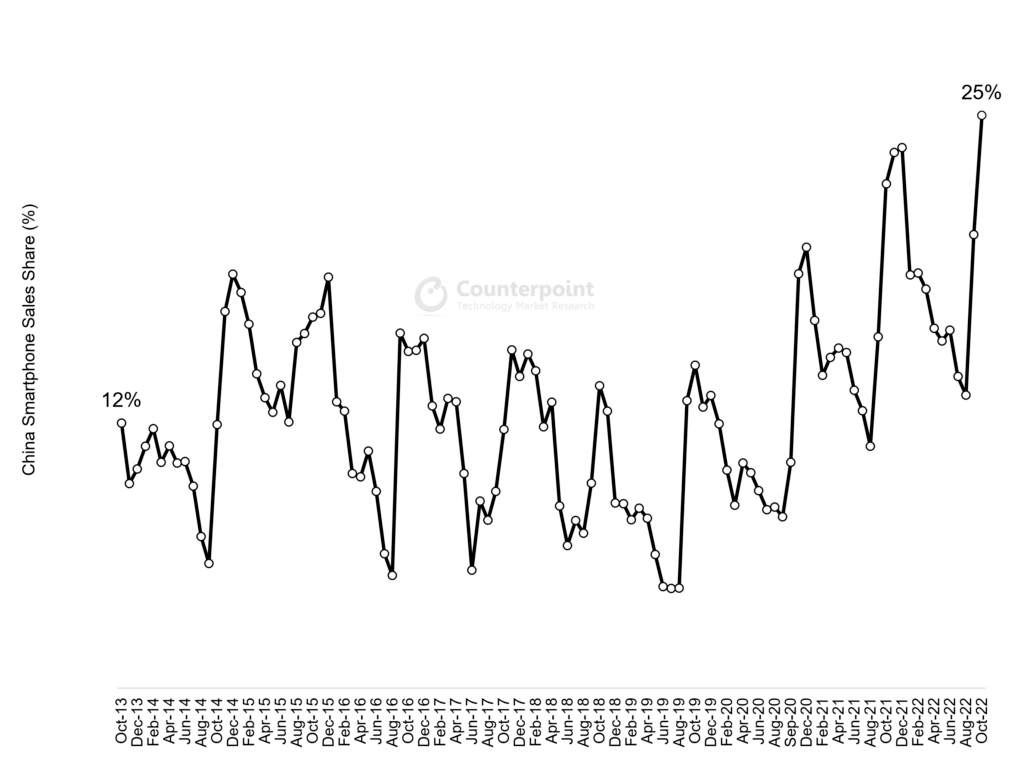
Apples market share in China.
Source: Counterpoint
Looking at the trend, the iPhone 14 series has started off well with the iPhone 14 Pro and Pro Max performing better than the previous generation. Qi noted that the iPhone 13 also continues to do well, as the iPhone 14 offers little differentiation from the iPhone 13. Adding to that, Senior Analyst Varun Mishra said, “The trend of rising Pro series popularity is not limited to China. It is there in other key markets like the US as well.”
However, analysts are also concerned about the recent manufacturing interruptions ahead of the holiday season. Counterpoint Research released guidance earlier saying delivery times for iPhone 14 Pro and Pro Max are significantly delayed. It said customers who ordered the phones last week could expect to wait 37 days for delivery, the longest wait time since the models launched. Apple’s regular iPhone 14 is still in stock.
There are even reports indicating that the unrest in Apple’s Foxconn factory in Zhengzhou could lead to a significant drop in year-end iPhone productions — by a staggering 6 million units. Much will depend on how quickly Foxconn Technology Group, the Taiwanese company that operates the facility, can get people back to assembly lines after violent protests against Covid restrictions.
If lockdowns continue in the weeks ahead, production could be set further back. The Zhengzhou campus, Apple’s world’s largest iPhone factory, has been wracked by lockdowns and worker unrest for weeks after Covid infections left Foxconn and the local government struggling to contain the outbreak. What made matters worse was the fact that thousands of staff fled in October after chronic food shortages, only to be replaced by new employees who rebelled against pay and quarantine practices.
In short, the situation is getting from bad to worse for the iPhone maker in China. Perhaps, as pundits claimed, these are the perils of having been largely dependent on China for its key manufacturing. Interestingly though, a Reuters analysis of Apple’s supply chain data shows China’s prominence in the company’s global manufacturing is declining — a data not so surprising for many considering how Apple have been shifting manufacturing elsewhere in Asia.
The Reuters report indicated that in the five years up to 2019, China was the primary location of 44% to 47% of its suppliers’ production sites, but that fell to 41% in 2020, and 36% in 2021. The data also shows how a diversification drive by Apple and its suppliers, with investments in India and Vietnam and increased procurement from Taiwan, the United States and elsewhere, is reshaping the global supply structure.
Analysts and academics however reckon that Apple will remain dependent on China for many years to come. For context, the concentration of suppliers in China mainly centers around Foxconn’s factory which accounts for 70% of iPhones made globally.
READ MORE
- Strategies for Democratizing GenAI
- The criticality of endpoint management in cybersecurity and operations
- Ethical AI: The renewed importance of safeguarding data and customer privacy in Generative AI applications
- How Japan balances AI-driven opportunities with cybersecurity needs
- Deploying SASE: Benchmarking your approach


