
Here’s how IBM’s quantum safe technology secures tomorrow
- The company unveiled the IBM Quantum Safe Roadmap in tandem with a suite of technologies designed to facilitate a seamless transition to secure critical data from potential future threats.
- The objective of IBM’s Quantum Safe Roadmap and its affiliated technology is to equip organizations with a holistic view of their cryptographic infrastructure.
IBM once made headlines by creating the world’s largest quantum computer, boasting 433 qubits, a technology capable of performing quantum computations far beyond the reach of any classical computer.
Fast forward to the present; at their annual Think conference, IBM unveiled their latest innovation: the IBM Quantum Safe technology. This end-to-end solution, comprising a comprehensive toolkit and IBM’s vast security expertise, is geared towards guiding organizations, including government agencies, on their journey towards quantum-safe readiness in the post-quantum era.
How IBM accelerates quantum-safe readiness for organizations and governments
As quantum technology progresses rapidly, it holds promise to tackle problems previously deemed unsolvable, benefiting both business and scientific domains. However, this advancement brings with it potential security threats. The evolving capabilities of quantum computers threaten to compromise even the most widely used security protocols globally.
In response, IBM has drawn upon its broad knowledge in cryptography, quantum computing, and critical infrastructure to craft the technology.
This array of capabilities is geared towards assisting clients in readying for the post-quantum era through:
- The IBM Quantum Safe Explorer: This tool allows organizations to probe source and object code to find cryptographic assets, dependencies, and vulnerabilities, creating a Cryptography Bill of Materials (CBOM). It provides teams with a centralized view of potential risks.
- The IBM Quantum Safe Advisor: This facilitates the creation of an active perspective on the cryptographic assets to guide the remediation process, while also assessing the cryptographic status and adherence to compliance to rank potential risks.
- The IBM Quantum Safe Remediator: This helps organizations to deploy and test quantum-safe remediation patterns, aiding in understanding potential impacts on systems and assets as they gear up for quantum-safe solutions deployment.
IBM is also revealing the IBM Quantum Safe Roadmap, a first-of-its-kind guide to help clients navigate this security transition. The roadmap delineates the technological milestones towards increasingly sophisticated quantum-safe technology designed to help organizations meet future cryptographic standards and safeguard systems from emerging vulnerabilities.
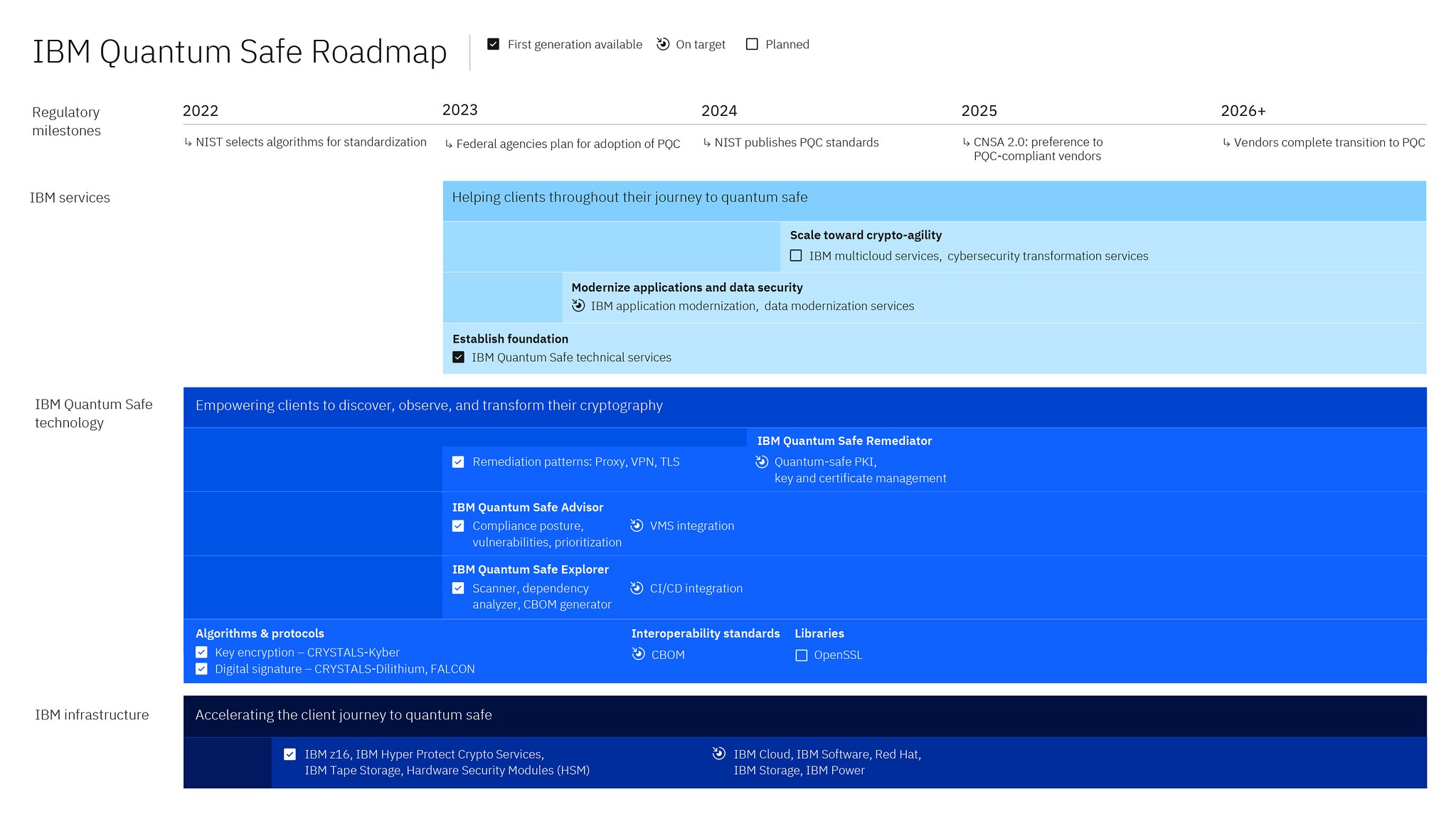
Source – IBM
This path involves three crucial steps:
- Discover: Identify cryptography usage, analyze dependencies, and create a CBOM.
- Observe: Evaluate the cryptographic stance of vulnerabilities and prioritize remediation based on risks.
- Transform: Carry out remediation and mitigation using crypto-agility and embedded automation.
Ray Harishankar, an IBM Fellow and the leader of IBM Quantum Safe technology, stressed the company’s commitment to addressing the crucial needs of clients as they prepare their cryptography for the quantum era. He said, “Our new suite of quantum-safe technologies and milestones laid out on our roadmap is designed for the continuous evolution of post-quantum security in tandem with useful quantum computing, including solutions to help industries navigate this shift effectively and easily.”
Partnerships to accelerate quantum safe technology
IBM partnered with Vodafone Group last year, focusing on quantum-safe cybersecurity. This partnership also saw Vodafone joining the IBM Quantum Network, thereby granting the multinational telecommunications corporation cloud access to IBM’s cutting-edge quantum computing systems and leading quantum expertise. Together, they aim to validate and advance potential quantum applications within the telecommunications industry.
As part of this collaboration, Vodafone will delve into the world of quantum computing, exploring its potential across various telecommunications scenarios. The company is committed to enhancing its workforce’s understanding of quantum technology via IBM-led iterative prototyping. It seeks to recruit quantum computing experts to establish a specialized capability within the organization.
Meanwhile, the U.S. government has been pushing federal agencies towards the quantum-safe transition through new guidelines and requirements. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has approved four quantum-resistant algorithms for standardization, with three developed by IBM alongside academic and industry collaborators.
The National Security Agency (NSA) established new requirements for national security systems to transition to quantum-safe algorithms by 2025. The White House also mandated federal agencies to compile an inventory of systems vulnerable to quantum-capable cryptographic threats.
IBM’s Quantum Safe Roadmap and associated technology aim to give organizations a comprehensive understanding of their cryptographic setup, thus facilitating the identification and address of changes that may be crucial for thriving in the post-quantum era.
READ MORE
- Ethical AI: The renewed importance of safeguarding data and customer privacy in Generative AI applications
- How Japan balances AI-driven opportunities with cybersecurity needs
- Deploying SASE: Benchmarking your approach
- Insurance everywhere all at once: the digital transformation of the APAC insurance industry
- Google parent Alphabet eyes HubSpot: A potential acquisition shaping the future of CRM


